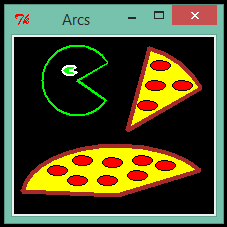
The first code is a simple example:
We must create a canvas using the "Canvas" method, also its dimensions are declared here.import Tkinter root = Tkinter.Tk() ch, cw = 200, 200 c1 = Tkinter.Canvas(root, height = ch, width = cw, bg = "black") c1.create_arc(30, 30, 200, 200, start = 30, extent = 45, outline = "brown", fill = "yellow", width = 4) c1.create_arc(10, 130, 200, 230, start = 30, extent = 145, outline = "brown", fill = "yellow", width = 4) c1.create_arc(30, 30, 100, 100, start = 30, extent = 295, outline = "green", width = 2) c1.create_arc(50, 50, 65, 60, start = 30, extent = 310, outline = "green", width = 2) c1.pack() root.title("Arcs") root.mainloop()
c1 = Tkinter.Canvas(root, height = ch, width = cw, bg = "black")
Then we create an arc by using:
c1.create_arc(30, 30, 200, 200, start = 30, extent = 45, outline = "brown", fill = "yellow", width = 4)
The coordinates of the first point are (30, 30), and of the last point are (200, 200). The attributes of outline_color and width_size go with "outline" and "width", respectively.
Then we could show the results in the screen by using the "pack" or "grid" methods.
 The next code has some variations.
The next code has some variations.
import Tkinter
def mz(x, y):
# Oval within a fixed space
c1.create_oval(x, y, x + 20, y + 10, fill = "red")
def arc(ax, ay, bx, by, s, e, w, o, f = None):
c1.create_arc( ax, ay, bx, by ,
start = s ,
extent = e ,
outline = o ,
fill = f ,
width = w )
root = Tkinter.Tk()
ch, cw = 200, 200
c1 = Tkinter.Canvas(root, height = ch, width = cw, bg = "black")
arc(30, 30, 200, 200, 30, 45, 4, "brown", "yellow")
arc(10, 130, 200, 230, 30, 145, 4, "brown", "yellow")
arc(50, 50, 65, 60, 30, 310, 2, "white", "green" )
arc(30, 30, 100, 100, 30, 295, 2, "green")
pts = [ [ 35, 150], [55, 160], [ 60, 140], [ 85, 160],
[ 90, 142], [115, 155], [120, 140], [125, 85],
[133, 65], [138, 45], [143, 145], [160, 65]
]
for n in range(len(pts)):
mz(pts[n][0], pts[n][1])
c1.pack()
root.title("Arcs")
root.mainloop()
 Second code sample is:
Second code sample is:
import Tkinter
def arc_fi(a, b, s, e, w):
ax, ay = a[0], a[1]
bx, by = b[0], b[1]
fc = "yellow" # fill color
c1.create_arc(ax, ay, bx, by, start = s, extent = e, fill = fc, width = w)
root = Tkinter.Tk()
ch, cw = 200, 200
c1 = Tkinter.Canvas(root, height = ch, width = cw, bg = "black")
for i in range(4, 7):
a = [10 * i, 10 * i]
b = [40 * i, 40 * i]
s = 15 * i
e = s + 15
arc_fi(a, b, s, e, 4)
c1.pack()
root.title("Rnd01")
root.mainloop()
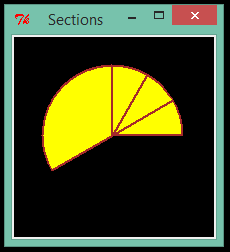
 Third code sample is:
Third code sample is:
import Tkinter
def arc_of(a, b, s, e, w):
ax, ay = a[0], a[1]
bx, by = b[0], b[1]
pts = [ax, ay, bx, by]
oc = "brown" # outline color
fc = "yellow" # fill color
c1.create_arc(pts, start = s, extent = e, outline = oc, fill = fc, width = w)
root = Tkinter.Tk()
ch, cw = 200, 200
c1 = Tkinter.Canvas(root, height = ch, width = cw, bg = "black")
for i in range(0, 4):
a = [30, 30]
b = [170, 170]
s = 30 * i
e = s + 30
arc_of(a, b, s, e, 2)
c1.pack()
root.title("Sections")
root.mainloop()

No comments:
Post a Comment