The next code is based on the Gauss Elimination method for solving a system of linear equations.
# Gauss elimination method for 2 linear equations
import Tkinter as tk
def lab_1(txt, foreground, row, col):
w = tk.Label(root, text = txt, fg = foreground)
w.grid(row = row, column = col)
return w
def lab_2(txt, row, col, cs):
w = tk.Label(root, text = txt)
w.grid(row = row, column = col, columnspan = cs)
return w
def lab_3(txt):
w = tk.Label(root, text = txt)
return w
def ent_1(txt_var, width_e, row, col):
w = tk.Entry(root, textvariable = txt_var, width = width_e)
w.grid(row = row, column = col)
return w
#tk.Button(root, text = "-> SOLVE", borderwidth = 4, command = solve_le)
def button(txt, border_width, cmd, row, col, rs, cs):
b = border_width
t = txt
w = tk.Button(root, text = t, borderwidth = b, command = cmd)
w.grid(row = row, column = col, rowspan = rs, columnspan = cs)
return w
def solve_le():
if a_val.get() == 0:
print "The value of 'a' must be greater than 0"
else:
a = a_val.get()
b = b_val.get()
c = c_val.get()
d = d_val.get()
e = e_val.get()
f = f_val.get()
nf = - d/a
d_n = nf * a + d
e_n = nf * b + e
f_n = nf * c + f
y = f_n / e_n
x = (c - b * y) / a
print "nf =", nf
x_result.config(text = x)
x_result.grid(row = 4, column = 3, sticky = tk.W, columnspan = 2)
y_result.config(text = y)
y_result.grid(row = 5, column = 3, sticky = tk.W, columnspan = 2)
""" Starting with Tkinter codes ... """
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Solving 2 Linear Equations")
w_lbl = 3
w_ent = 19
b_txt = "-> SOLVE"
b_brw = 4
b_row = 4
b_col = 0
span1 = 2
span2 = 5
RED = "red"
BLUE = "blue"
a_val, b_val, c_val = tk.DoubleVar(), tk.DoubleVar(), tk.DoubleVar()
d_val, e_val, f_val = tk.DoubleVar(), tk.DoubleVar(), tk.DoubleVar()
eq_1_str = " A * x + B * y = C"
eq_2_str = " D * x + E * y = F"
lab_2(eq_1_str, 0, 0, span2)
lab_2(eq_2_str, 1, 0, span2)
""" <<<< Entries >>>> """
ent_1(a_val, w_ent, 2, 0)
ent_1(b_val, w_ent, 2, 2)
ent_1(c_val, w_ent, 2, 4)
ent_1(d_val, w_ent, 3, 0)
ent_1(e_val, w_ent, 3, 2)
ent_1(f_val, w_ent, 3, 4)
""" <<<< Labels >>>> """
lab_1(" x +" , RED, 2, 1)
lab_1(" y = ", RED, 2, 3)
lab_1(" x +" , BLUE, 3, 1)
lab_1(" y = ", BLUE, 3, 3)
lab_1(" x = ", BLUE, 4, 2)
lab_1(" y = ", BLUE, 5, 2)
x_result = lab_3(" ")
y_result = lab_3(" ")
""" <<<< Button >>>> """
button(b_txt, b_brw, solve_le, b_row, b_col, span1, span1)
root.mainloop()
The results are going to be approximations because of the nature of the code, naturally.
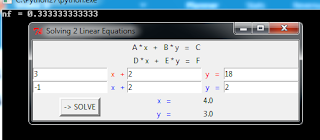
Testing with the next pair of equations:
3 * x1 + 2 * x2 = 18 (-1) * x1 + 2 * x2 = 2


No comments:
Post a Comment